The following program implements all features of Data Structures STACK, QUEUE and LIST using generic functions (templates in C++). User have choice for selection the data type float,integer or character to use the data structures. Also there is a game which takes 3 positive integers as input a,b and c. a represent the number of digits, b represent the maximum sum of digits and c represent the maximum total sum of all the numbers formed during the game. The score of the game is the highest number formed. The user after inputting the parameters will sequentially enter the digits, and the game will automatically stops when the sum of the numbers formed exceeds c. For example is user enter 3,13,200 as parameters and the digits entered sequentially is 1,1,9,5,9,6,5,4, 8,9.... the numbers that will be stored in the stack will be 119,5,9,11,12,9.... using the restrictions. The stack is then sorted using another stack and the top element is your score. The Game is generalized for decimal numbers also i.e., input can be 1,1,.,9,5,.9,...... so on.
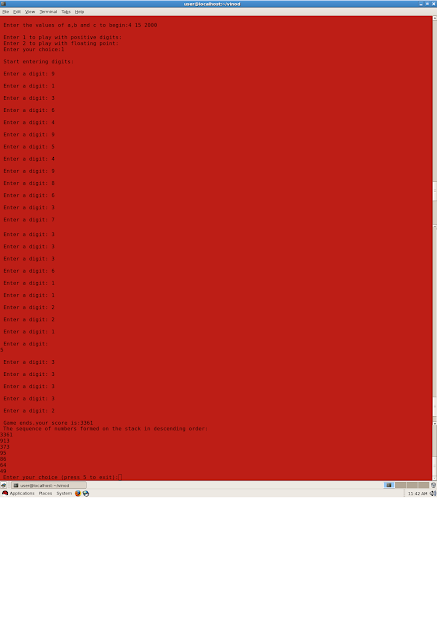
Here is an sample output:
Here is the link for the code http://sdrv.ms/16Wrw8x
C++ Code
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
void f1(void);
void f2(void);
void f3(void);
void f4(void);
template <class L> class List
{
private:
L d;
L *data;
int i;
public:
List(){}
List (int n)
{
data=new L[n];
i=0;
}
void store()
{
cin>>d;
data[i]=d;
i++;
}
void display(int n)
{
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
cout<<"\t"<<data[i];
}
};
template <class L>
class Stack: virtual public List<L>
{
protected:
L *data;
int top;
public:
Stack(){}
Stack (int n)
{
data=new L[n];
top=-1;
}
//static int t;
void push(L,int);
void pop(int *pund,L *x);
};
//template<class L>int Stack::t=-1;
template<class L>
void Stack<L>::push(L x,int STACKSIZE)
{
if(top==STACKSIZE-1)
{
cout<<"\n Stack is full, element not inserted:";
return;
}
else
data[++top]=x;
}
template<class L>
void Stack<L>::pop(int *pund, L *x)
{
if(top==-1)
{
*pund=TRUE;
return;
}
else
{
*x=data[top--];
*pund=FALSE;
return;
}
}
template<class L>
class Queue: virtual public List<L>
{
protected:
L *data;
int front;
int rear;
public:
Queue(){}
Queue(int MAXQUEUE)
{
data=new L[MAXQUEUE];
front=rear=MAXQUEUE-1;
}
void insert(int MAXQUEUE,L x);
void remove(L *x,int *pund,int MAXQUEUE);
};
template<class L>
void Queue<L>::remove(L *x,int *pund,int MAXQUEUE)
{
if(rear==front)
{
cout<<"\n Queue is empty:";
*pund=TRUE;
return;
}
if(front==MAXQUEUE-1)
front=0;
else
front++;
*x=data[front];
return;
}
template<class L>
void Queue<L>::insert(int MAXQUEUE,L x)
{
if(rear==MAXQUEUE-1)
rear=0;
else
rear++;
if(rear==front)
{
cout<<"\n Queue overflow, element not inserted:";
return;
}
data[rear]=x;
return;
}
template<class L>
class GAME:public Stack<L>,public Queue<L>
{
protected:
L *digits;
int tdigits;
L dsum;
L tsum;
public:
GAME(int a,int b,int c)
{ tdigits=a; dsum=b; tsum=c; }
GAME():Stack<L>(400),Queue<L>(400)
{ digits= new L[400]; }
void enter_digits(GAME,GAME,bool);
};
template<class L>
void GAME<L>::enter_digits(GAME s2,GAME s3,bool FLAG)
{
int und,pund=FALSE,len,k;
int i=0,j=0,FLAG1=TRUE,dg=0,DFLAG=0,DCOUNT,count=0;
L y,x,a,numb=0,sumd=0,tmp=0,sumt=0,numb1=0;
char t[10],dot[3];
if(FLAG)
{
do
{
for(i=0;i<tdigits;i++)
{
cout<<"\n Enter a digit: ";
cin>>t;
len=strlen(t);
if(!atoi(t) && atoi(t) != 0)
{
i--;
cout<<"\n You must enter a digit:\n";
continue;
}
if(len>1)
{
i--;
cout<<"\n You must enter a digit:\n";
continue;
}
a=atoi(t);
s2.insert(400,a);
}
do
{
if(sumd>dsum)
break;
else
{
if(FLAG1==TRUE)
numb=tmp+numb*10;
s2.remove(&x,&und,400);
numb=x+numb*10;
sumd=sumd+x;
if(sumd>dsum)
{
tmp=x;
FLAG1=TRUE;
sumd -=x;
break;
}
tmp=0;
}
FLAG1=FALSE;
j++;
}while(j<tdigits);
if(FLAG1==TRUE)
{j=1;numb=numb/10;}
else
{j=0;}
//cout<<"\n <Number>"<<numb;
s2.pop(&pund,&y);
if(pund==TRUE)
s2.push(numb,400);
else
{
if(numb>=y)
{
s2.push(y,400);
s2.push(numb,400);
}
else
{
s3.push(y,400);
while(y>numb)
{
s2.pop(&pund,&y);
if(pund==TRUE || y<=numb)
{
if(pund==TRUE)
{break;}
else
{s2.push(y,400); break;}
}
s3.push(y,400);
}
s2.push(numb,400);
while(1)
{
s3.pop(&pund,&y);
if(pund==TRUE)
break;
s2.push(y,400);
}
}
}
sumt +=numb;
sumd=tmp;
numb=0;
}while(sumt<=tsum);
s2.pop(&pund,&y);
cout<<"\n Game ends,your score is:"<<y;
cout<<"\n The sequence of numbers formed on the stack in descending order:\n";
while(1)
{
cout<<y;
s2.pop(&pund,&y);
if(pund==TRUE)
break;
cout<<"\n";
}
}//end of integer game
else
{
strcpy(dot,"$");
do
{
for(i=0;i<tdigits;i++)
{
cout<<"\n Enter the number:";
cin>>t;
//cout<<strlen(t);
if(strlen(t)>=2)
{
cout<<"\n Not a valid input:";
i--;
continue;
}
if(strcmp(dot,t)==0)
{
i--;
cout<<"\n Two consecutive dots not allowed:";
continue;
}
if(strcmp(t,".")==0)
{
strcpy(dot,t);
a=-1.0;
s2.insert(400,a);
continue;
}
if(!atof(t) || !atoi(t))
{
cout<<"\n Not a valid input:";
i--;
continue;
}
j=0;
while(t[j]!='\0' && strlen(t)<2)
{
a=atof(t);
s2.insert(400,a);
j++;
}
strcpy(dot,"$");
} //end of one set of input
und=TRUE;
while(und)
{
s2.remove(&x,&und,400);
if(x==-1)
{
DCOUNT++;
DFLAG=TRUE;
j=1;
if(DCOUNT==2)
break;
}//end of if
else
{
if(DFLAG==TRUE)
{
sumd +=x;
if(sumd>dsum)
{
tmp=x;
DFLAG=FALSE;
break;
}
count++;
numb1=numb1+x*pow(10,-j);
j++;
if(count==tdigits)
break;
}//end of if
else
{
sumd +=x;
if(sumd>dsum)
{
tmp=x;
break;
}
count++;
numb=x+numb*10;
}//end of inner else
if(count==tdigits)
break;
}//end of else
cout<<"\n Sumd="<<sumd;
cout<<"\n Count="<<count;
cout<<"\n J="<<j;
cout<<"\n DFLAG="<<DFLAG;
} //end of while(und)
count=0;
numb=numb+numb1;
cout<<"\n <Number>\n"<<numb;
sumt +=numb;
numb=0.0;
numb1=0.0;
if(DFLAG==TRUE && tmp!=0)
{
count++;
numb1=numb1+tmp*pow(10,-j);
sumd=tmp;
}
if(DFLAG==FALSE && tmp!=0)
{
count++;
numb=tmp+numb*10;
sumd=tmp;
}
}while(sumt<70.0);
}//end of float game
}
int main()
{
int menu;
cout<<"\n Press '1' for LIST:";
cout<<"\n Press '2' for STACK:";
cout<<"\n Press '3' for QUEUE:";
cout<<"\n Press '4' to play the GAME:";
cout<<"\n Press '5' to exit:";
do{
cout<<"\n Enter your choice:";
cin>>menu;
switch(menu)
{
case 1:
f1();
break;
case 2:
f2();
break;
case 3:
f3();
break;
case 4:
f4();
break;
default:
break;
}
}while(menu!=5);
return 0;
}
void f4(void)
{
int a,b,c,ch;
bool FLAG;
cout<<"\n Enter the values of a,b and c to begin:";
cin>>a>>b>>c;
GAME <int>s1(a,b,c); GAME<int>s2;GAME <int>s3;
GAME <float>t1(a,b,c); GAME <float>t2; GAME <float>t3;
cout<<"\n Enter 1 to play with positive digits:";
cout<<"\n Enter 2 to play with floating point:";
cout<<"\n Enter your choice:";
cin>>ch;
if(ch==1)
{
FLAG=1;
cout<<"\n Start entering digits:\n";
s1.enter_digits(s2,s3,FLAG);
}
if(ch==2)
{
FLAG=0;
cout<<"\n Start entering digits:\n";
t1.enter_digits(t2,t3,FLAG);
}
}
void f3(void)
{
int n,choice,x,und,ch;
Queue <int>Q1(n);
Queue <float>Q2(n);
float x1;
cout<<"\n Enter the size of the QUEUE:";
cin>>n;
cout<<"\n Enter 1 to add integer values to QUEUE:";
cout<<"\n Enter 2 to add floating point values to QUEUE:";
cout<<"\n Enter your choice:";
cin>>ch;
if(ch==1)
{
cout<<"\n Press 1 to insert an element in the Queue:";
cout<<"\n Press 2 to remove an element from the Queue:";
cout<<"\n Press 3 to exit:";
do
{
cout<<"\n Enter your choice for menu:";
cin>>choice;
switch(choice)
{
case 1:
cout<<"\n Enter the element:";
cin>>x;
Q1.insert(n,x);
break;
case 2:
Q1.remove(&x,&und,n);
if(und==TRUE)
{
// cout<<"\n Queue Underflow:";
break;
}
else
cout<<"\n Element removed is: "<<x;
break;
default:
break;
}
} while(choice!=3);
}
if(ch==2)
{
cout<<"\n Press 1 to insert an element in the Queue:";
cout<<"\n Press 2 to remove an element from the Queue:";
cout<<"\n Press 3 to exit:";
do
{
cout<<"\n Enter your choice for menu:";
cin>>choice;
switch(choice)
{
case 1:
cout<<"\n Enter the element:";
cin>>x;
Q2.insert(n,x1);
break;
case 2:
Q2.remove(&x1,&und,n);
if(und==TRUE)
{
// cout<<"\n Queue Underflow:";
break;
}
else
cout<<"\n Element removed is: "<<x1;
break;
default:
break;
}
} while(choice!=3);
}
}
void f2(void)
{
int n,choice,x,und,ch;
Stack <int>S1(n);
Stack <float>S2(n);
float x1;
cout<<"\n Enter the size of the STACK:"<<endl;
cin>>n;
cout<<"\n Enter 1 to add integer values to List:";
cout<<"\n Enter 2 to add floating point values to List:";
cout<<"\n Enter your choice:";
cin>>ch;
if(ch==1)
{
cout<<"\n Press 1 to push an element in the stack:";
cout<<"\n Press 2 to pop an element:";
cout<<"\n Press 3 to exit:";
do
{
cout<<"\n Enter your choice for menu:";
cin>>choice;
switch(choice)
{
case 1:
cout<<"\n Enter the element:";
cin>>x;
S1.push(x,n);
break;
case 2:
S1.pop(&und,&x);
if(und==TRUE)
{
cout<<"\n Stack Underflow:";
break;
}
else
cout<<"\n Element popped out is: "<<x;
break;
default:
break;
}
} while(choice!=3);
}
if(ch==2)
{
cout<<"\n Press 1 to push an element in the stack:";
cout<<"\n Press 2 to pop an element:";
cout<<"\n Press 3 to exit:";
do
{
cout<<"\n Enter your choice for menu:";
cin>>choice;
switch(choice)
{
case 1:
cout<<"\n Enter the element:";
cin>>x1;
S2.push(x1,n);
break;
case 2:
S2.pop(&und,&x1);
if(und==TRUE)
{
cout<<"\n Stack Underflow:";
break;
}
else
cout<<"\n Element popped out is: "<<x1;
break;
default:
break;
}
} while(choice!=3);
}
}
void f1(void)
{
int n,nf=0,choice;;
char c;
List <int> Ls(n);
List <float>Ls1(n);
List <char>Ls2(n);
cout<<"\n Enter the number of elements to be stored in the list:"<<endl;
cin>>n;
cout<<"\n Enter 1 to add integer values to List:";
cout<<"\n Enter 2 to add floating point values to List:";
cout<<"\n Enter 3 to add character values to List:";
cout<<"\n Enter your choice:";
cin>>choice;
if(choice==1)
{
do
{
cout<<"\n Enter the element in the list:";
Ls.store();
nf++;
if(nf==n)
{
cout<<"\n No more elements can be added:";
break;
}
cout<<"\n Do you wish to enter another element (y/n):";
cin>>c;
}while (c!='n');
cout<<"\n Press 'v' to view the list or any other key to exit:";
cin>>c;
if(c=='v')
Ls.display(nf);
}
if(choice==2)
{
do
{
cout<<"\n Enter the element in the list:";
Ls1.store();
nf++;
if(nf==n)
{
cout<<"\n No more elements can be added:";
break;
}
cout<<"\n Do you wish to enter another element (y/n):";
cin>>c;
}while (c!='n');
cout<<"\n Press 'v' to view the list or any other key to exit:";
cin>>c;
if(c=='v')
Ls1.display(nf);
}
if(choice==3)
{
List <char>Ls[n];
do
{
cout<<"\n Enter the element in the list:";
Ls2.store();
nf++;
if(nf==n)
{
cout<<"\n No more elements can be added:";
break;
}
cout<<"\n Do you wish to enter another element (y/n):";
cin>>c;
}while (c!='n');
cout<<"\n Press 'v' to view the list or any other key to exit:";
cin>>c;
if(c=='v')
Ls2.display(nf);
}
}
Here is an sample output:
Here is the link for the code http://sdrv.ms/16Wrw8x
C++ Code
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
void f1(void);
void f2(void);
void f3(void);
void f4(void);
template <class L> class List
{
private:
L d;
L *data;
int i;
public:
List(){}
List (int n)
{
data=new L[n];
i=0;
}
void store()
{
cin>>d;
data[i]=d;
i++;
}
void display(int n)
{
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
cout<<"\t"<<data[i];
}
};
template <class L>
class Stack: virtual public List<L>
{
protected:
L *data;
int top;
public:
Stack(){}
Stack (int n)
{
data=new L[n];
top=-1;
}
//static int t;
void push(L,int);
void pop(int *pund,L *x);
};
//template<class L>int Stack::t=-1;
template<class L>
void Stack<L>::push(L x,int STACKSIZE)
{
if(top==STACKSIZE-1)
{
cout<<"\n Stack is full, element not inserted:";
return;
}
else
data[++top]=x;
}
template<class L>
void Stack<L>::pop(int *pund, L *x)
{
if(top==-1)
{
*pund=TRUE;
return;
}
else
{
*x=data[top--];
*pund=FALSE;
return;
}
}
template<class L>
class Queue: virtual public List<L>
{
protected:
L *data;
int front;
int rear;
public:
Queue(){}
Queue(int MAXQUEUE)
{
data=new L[MAXQUEUE];
front=rear=MAXQUEUE-1;
}
void insert(int MAXQUEUE,L x);
void remove(L *x,int *pund,int MAXQUEUE);
};
template<class L>
void Queue<L>::remove(L *x,int *pund,int MAXQUEUE)
{
if(rear==front)
{
cout<<"\n Queue is empty:";
*pund=TRUE;
return;
}
if(front==MAXQUEUE-1)
front=0;
else
front++;
*x=data[front];
return;
}
template<class L>
void Queue<L>::insert(int MAXQUEUE,L x)
{
if(rear==MAXQUEUE-1)
rear=0;
else
rear++;
if(rear==front)
{
cout<<"\n Queue overflow, element not inserted:";
return;
}
data[rear]=x;
return;
}
template<class L>
class GAME:public Stack<L>,public Queue<L>
{
protected:
L *digits;
int tdigits;
L dsum;
L tsum;
public:
GAME(int a,int b,int c)
{ tdigits=a; dsum=b; tsum=c; }
GAME():Stack<L>(400),Queue<L>(400)
{ digits= new L[400]; }
void enter_digits(GAME,GAME,bool);
};
template<class L>
void GAME<L>::enter_digits(GAME s2,GAME s3,bool FLAG)
{
int und,pund=FALSE,len,k;
int i=0,j=0,FLAG1=TRUE,dg=0,DFLAG=0,DCOUNT,count=0;
L y,x,a,numb=0,sumd=0,tmp=0,sumt=0,numb1=0;
char t[10],dot[3];
if(FLAG)
{
do
{
for(i=0;i<tdigits;i++)
{
cout<<"\n Enter a digit: ";
cin>>t;
len=strlen(t);
if(!atoi(t) && atoi(t) != 0)
{
i--;
cout<<"\n You must enter a digit:\n";
continue;
}
if(len>1)
{
i--;
cout<<"\n You must enter a digit:\n";
continue;
}
a=atoi(t);
s2.insert(400,a);
}
do
{
if(sumd>dsum)
break;
else
{
if(FLAG1==TRUE)
numb=tmp+numb*10;
s2.remove(&x,&und,400);
numb=x+numb*10;
sumd=sumd+x;
if(sumd>dsum)
{
tmp=x;
FLAG1=TRUE;
sumd -=x;
break;
}
tmp=0;
}
FLAG1=FALSE;
j++;
}while(j<tdigits);
if(FLAG1==TRUE)
{j=1;numb=numb/10;}
else
{j=0;}
//cout<<"\n <Number>"<<numb;
s2.pop(&pund,&y);
if(pund==TRUE)
s2.push(numb,400);
else
{
if(numb>=y)
{
s2.push(y,400);
s2.push(numb,400);
}
else
{
s3.push(y,400);
while(y>numb)
{
s2.pop(&pund,&y);
if(pund==TRUE || y<=numb)
{
if(pund==TRUE)
{break;}
else
{s2.push(y,400); break;}
}
s3.push(y,400);
}
s2.push(numb,400);
while(1)
{
s3.pop(&pund,&y);
if(pund==TRUE)
break;
s2.push(y,400);
}
}
}
sumt +=numb;
sumd=tmp;
numb=0;
}while(sumt<=tsum);
s2.pop(&pund,&y);
cout<<"\n Game ends,your score is:"<<y;
cout<<"\n The sequence of numbers formed on the stack in descending order:\n";
while(1)
{
cout<<y;
s2.pop(&pund,&y);
if(pund==TRUE)
break;
cout<<"\n";
}
}//end of integer game
else
{
strcpy(dot,"$");
do
{
for(i=0;i<tdigits;i++)
{
cout<<"\n Enter the number:";
cin>>t;
//cout<<strlen(t);
if(strlen(t)>=2)
{
cout<<"\n Not a valid input:";
i--;
continue;
}
if(strcmp(dot,t)==0)
{
i--;
cout<<"\n Two consecutive dots not allowed:";
continue;
}
if(strcmp(t,".")==0)
{
strcpy(dot,t);
a=-1.0;
s2.insert(400,a);
continue;
}
if(!atof(t) || !atoi(t))
{
cout<<"\n Not a valid input:";
i--;
continue;
}
j=0;
while(t[j]!='\0' && strlen(t)<2)
{
a=atof(t);
s2.insert(400,a);
j++;
}
strcpy(dot,"$");
} //end of one set of input
und=TRUE;
while(und)
{
s2.remove(&x,&und,400);
if(x==-1)
{
DCOUNT++;
DFLAG=TRUE;
j=1;
if(DCOUNT==2)
break;
}//end of if
else
{
if(DFLAG==TRUE)
{
sumd +=x;
if(sumd>dsum)
{
tmp=x;
DFLAG=FALSE;
break;
}
count++;
numb1=numb1+x*pow(10,-j);
j++;
if(count==tdigits)
break;
}//end of if
else
{
sumd +=x;
if(sumd>dsum)
{
tmp=x;
break;
}
count++;
numb=x+numb*10;
}//end of inner else
if(count==tdigits)
break;
}//end of else
cout<<"\n Sumd="<<sumd;
cout<<"\n Count="<<count;
cout<<"\n J="<<j;
cout<<"\n DFLAG="<<DFLAG;
} //end of while(und)
count=0;
numb=numb+numb1;
cout<<"\n <Number>\n"<<numb;
sumt +=numb;
numb=0.0;
numb1=0.0;
if(DFLAG==TRUE && tmp!=0)
{
count++;
numb1=numb1+tmp*pow(10,-j);
sumd=tmp;
}
if(DFLAG==FALSE && tmp!=0)
{
count++;
numb=tmp+numb*10;
sumd=tmp;
}
}while(sumt<70.0);
}//end of float game
}
int main()
{
int menu;
cout<<"\n Press '1' for LIST:";
cout<<"\n Press '2' for STACK:";
cout<<"\n Press '3' for QUEUE:";
cout<<"\n Press '4' to play the GAME:";
cout<<"\n Press '5' to exit:";
do{
cout<<"\n Enter your choice:";
cin>>menu;
switch(menu)
{
case 1:
f1();
break;
case 2:
f2();
break;
case 3:
f3();
break;
case 4:
f4();
break;
default:
break;
}
}while(menu!=5);
return 0;
}
void f4(void)
{
int a,b,c,ch;
bool FLAG;
cout<<"\n Enter the values of a,b and c to begin:";
cin>>a>>b>>c;
GAME <int>s1(a,b,c); GAME<int>s2;GAME <int>s3;
GAME <float>t1(a,b,c); GAME <float>t2; GAME <float>t3;
cout<<"\n Enter 1 to play with positive digits:";
cout<<"\n Enter 2 to play with floating point:";
cout<<"\n Enter your choice:";
cin>>ch;
if(ch==1)
{
FLAG=1;
cout<<"\n Start entering digits:\n";
s1.enter_digits(s2,s3,FLAG);
}
if(ch==2)
{
FLAG=0;
cout<<"\n Start entering digits:\n";
t1.enter_digits(t2,t3,FLAG);
}
}
void f3(void)
{
int n,choice,x,und,ch;
Queue <int>Q1(n);
Queue <float>Q2(n);
float x1;
cout<<"\n Enter the size of the QUEUE:";
cin>>n;
cout<<"\n Enter 1 to add integer values to QUEUE:";
cout<<"\n Enter 2 to add floating point values to QUEUE:";
cout<<"\n Enter your choice:";
cin>>ch;
if(ch==1)
{
cout<<"\n Press 1 to insert an element in the Queue:";
cout<<"\n Press 2 to remove an element from the Queue:";
cout<<"\n Press 3 to exit:";
do
{
cout<<"\n Enter your choice for menu:";
cin>>choice;
switch(choice)
{
case 1:
cout<<"\n Enter the element:";
cin>>x;
Q1.insert(n,x);
break;
case 2:
Q1.remove(&x,&und,n);
if(und==TRUE)
{
// cout<<"\n Queue Underflow:";
break;
}
else
cout<<"\n Element removed is: "<<x;
break;
default:
break;
}
} while(choice!=3);
}
if(ch==2)
{
cout<<"\n Press 1 to insert an element in the Queue:";
cout<<"\n Press 2 to remove an element from the Queue:";
cout<<"\n Press 3 to exit:";
do
{
cout<<"\n Enter your choice for menu:";
cin>>choice;
switch(choice)
{
case 1:
cout<<"\n Enter the element:";
cin>>x;
Q2.insert(n,x1);
break;
case 2:
Q2.remove(&x1,&und,n);
if(und==TRUE)
{
// cout<<"\n Queue Underflow:";
break;
}
else
cout<<"\n Element removed is: "<<x1;
break;
default:
break;
}
} while(choice!=3);
}
}
void f2(void)
{
int n,choice,x,und,ch;
Stack <int>S1(n);
Stack <float>S2(n);
float x1;
cout<<"\n Enter the size of the STACK:"<<endl;
cin>>n;
cout<<"\n Enter 1 to add integer values to List:";
cout<<"\n Enter 2 to add floating point values to List:";
cout<<"\n Enter your choice:";
cin>>ch;
if(ch==1)
{
cout<<"\n Press 1 to push an element in the stack:";
cout<<"\n Press 2 to pop an element:";
cout<<"\n Press 3 to exit:";
do
{
cout<<"\n Enter your choice for menu:";
cin>>choice;
switch(choice)
{
case 1:
cout<<"\n Enter the element:";
cin>>x;
S1.push(x,n);
break;
case 2:
S1.pop(&und,&x);
if(und==TRUE)
{
cout<<"\n Stack Underflow:";
break;
}
else
cout<<"\n Element popped out is: "<<x;
break;
default:
break;
}
} while(choice!=3);
}
if(ch==2)
{
cout<<"\n Press 1 to push an element in the stack:";
cout<<"\n Press 2 to pop an element:";
cout<<"\n Press 3 to exit:";
do
{
cout<<"\n Enter your choice for menu:";
cin>>choice;
switch(choice)
{
case 1:
cout<<"\n Enter the element:";
cin>>x1;
S2.push(x1,n);
break;
case 2:
S2.pop(&und,&x1);
if(und==TRUE)
{
cout<<"\n Stack Underflow:";
break;
}
else
cout<<"\n Element popped out is: "<<x1;
break;
default:
break;
}
} while(choice!=3);
}
}
void f1(void)
{
int n,nf=0,choice;;
char c;
List <int> Ls(n);
List <float>Ls1(n);
List <char>Ls2(n);
cout<<"\n Enter the number of elements to be stored in the list:"<<endl;
cin>>n;
cout<<"\n Enter 1 to add integer values to List:";
cout<<"\n Enter 2 to add floating point values to List:";
cout<<"\n Enter 3 to add character values to List:";
cout<<"\n Enter your choice:";
cin>>choice;
if(choice==1)
{
do
{
cout<<"\n Enter the element in the list:";
Ls.store();
nf++;
if(nf==n)
{
cout<<"\n No more elements can be added:";
break;
}
cout<<"\n Do you wish to enter another element (y/n):";
cin>>c;
}while (c!='n');
cout<<"\n Press 'v' to view the list or any other key to exit:";
cin>>c;
if(c=='v')
Ls.display(nf);
}
if(choice==2)
{
do
{
cout<<"\n Enter the element in the list:";
Ls1.store();
nf++;
if(nf==n)
{
cout<<"\n No more elements can be added:";
break;
}
cout<<"\n Do you wish to enter another element (y/n):";
cin>>c;
}while (c!='n');
cout<<"\n Press 'v' to view the list or any other key to exit:";
cin>>c;
if(c=='v')
Ls1.display(nf);
}
if(choice==3)
{
List <char>Ls[n];
do
{
cout<<"\n Enter the element in the list:";
Ls2.store();
nf++;
if(nf==n)
{
cout<<"\n No more elements can be added:";
break;
}
cout<<"\n Do you wish to enter another element (y/n):";
cin>>c;
}while (c!='n');
cout<<"\n Press 'v' to view the list or any other key to exit:";
cin>>c;
if(c=='v')
Ls2.display(nf);
}
}